- 前置き
- NGINX Ingress Controllerとは
- お気持ち
- 全体像
- 実装の話
- ingress-nginx-controller ${#ingress-nginx-controller}
- ビルド
- controller本体 ${#controller}
- マニフェスト
- main.go
- internal/ingress/controller/nginx.go
- func NewNGINXController(*Configuration, metric.Collector) *NGINXController ${#NewNGINXController}
- func (*NGINXController) Start() ${#controller-start}
- func (*NGINXController) Stop() error
- func (*NGINXController) syncIngress(interface${}) error ${#syncIngress}
- Admission Controller ${#admission-controller}
- (*NGINXController) CheckIngress(*networking.Ingress) error
- Leader Election ${#leader-election}
- wait-shutdown ${#wait-shutdown}
- dbg ${#dbg}
- ingress-nginx-admission-create ${#ingress-nginx-admission-create}
- ingress-nginx-admission-patch ${#ingress-nginx-admission-patch}
- jettech/kube-webhook-certgen
前置き
ここで書いている内容は全ての事は書いてないし気になったところだけを順番に見ている。
公開後は随時追記や修正をしていくつもりである。
間違っている箇所があったりしたらTwitter(@let_constant)へDMとかで教えてください。
| 日付 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 2020-07-19 | ingress-nginx-2.7.0 の内容で公開 |
NGINX Ingress Controllerとは
NginxをベースイメージとしてリバースプロキシやLBとして動作するIngress実装である。
L7で動作するのでホスト名やパスでのルーティング、SSLのオフロード等が実現できる。
他のIngress実装はTraefikやContourがあり、ここにまとめられている。
お気持ち
ServiceはClusterIPで公開する限りServiceにIPが振られるのでIngressはそれを見ていると思っていた。
ではそうなるとSticky Sessionsはどうやって実現しているのか不思議になった。
How it worksを読むと普通に書いてあるが、Endpointsを使用している。
これを知った時感動した。
Nginx IngressがServiceじゃなくてEndpoints見てるって知った時感動したよね
— さかもとりょーた(25) (@let_constant) May 27, 2020
ところで Nginx Ingress Controller のことを nginx-ingress なのか ingress-nginx って言えばいいのかいつもわからなくなる。正解を知りたい。
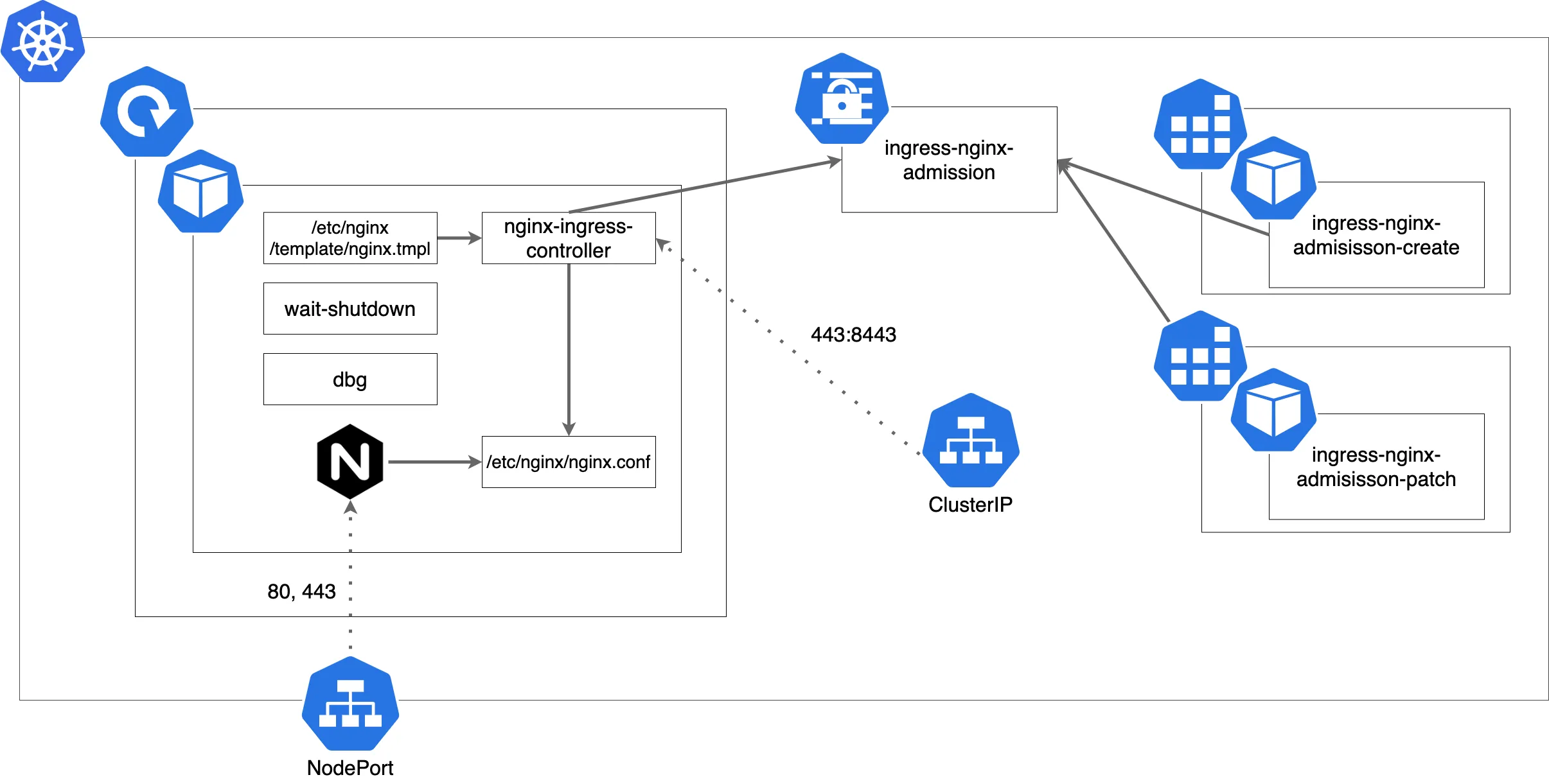
全体像
まずは大まかな全体像の図を貼る。
NodePort で公開されていたり、Job により Secret が生成されていたりする。
実装の話
バージョンは2020-06-21(日)時点で最新のingress-nginx-2.7.0
マニフェストはbaremetal/deploy.yaml
マニフェストを見るとcontrollerのDeploymentやJobが動いている事がわかる。
Podとして動いているものを順番に見ていく事にする。
ingress-nginx-controller {#ingress-nginx-controller}
イメージとしては下記のような順番で生成されている。
alpine:3.11- quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx:e3c49c52f4b74fe47ad65d6f3266a02e8b6b622f
- quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.33.0
ビルド
ビルドは build/build.sh で行なっていて3つのバイナリを作っている。
- nginx-ingress-controller はcontroller本体
- wait-shutdown は
preStopで叩いている - dbg はnginxの状態を検査するデバッグ用のツールである
go build \
-ldflags "-s -w \
-X ${PKG}/version.RELEASE=${TAG} \
-X ${PKG}/version.COMMIT=${GIT_COMMIT} \
-X ${PKG}/version.REPO=${REPO_INFO}" \
-o "rootfs/bin/${ARCH}/nginx-ingress-controller" "${PKG}/cmd/nginx"
go build \
-ldflags "-s -w \
-X ${PKG}/version.RELEASE=${TAG} \
-X ${PKG}/version.COMMIT=${GIT_COMMIT} \
-X ${PKG}/version.REPO=${REPO_INFO}" \
-o "rootfs/bin/${ARCH}/dbg" "${PKG}/cmd/dbg"
go build \
-ldflags "-s -w \
-X ${PKG}/version.RELEASE=${TAG} \
-X ${PKG}/version.COMMIT=${GIT_COMMIT} \
-X ${PKG}/version.REPO=${REPO_INFO}" \
-o "rootfs/bin/${ARCH}/wait-shutdown" "${PKG}/cmd/waitshutdown"- nginxのバイナリは images/nginx/rootfs/build.sh で行なっていて、モジュール等のバージョンが書いてある。
controller本体 {#controller}
マニフェスト
提供されているマニフェストでは下記のような引数で起動している。
全ての引数の詳細はCommand line argumentsに書いてある。
--election-idはHPAやreplica数を増やした場合にリーダー選出するためのidである、リーダー選出する実装についてはここ--ingress-classはクラスタ内で複数のIngress Controllerを動かしている際に指定が必要になる、GKEを使ってる場合とかはちゃんと指定する必要がある--validating-webhookはAdmission Controllerを起動してシンタックスエラーがないか等を調べる、指定しない場合は起動されない
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --election-id=ingress-controller-leader
- --ingress-class=nginx
- --configmap=ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx-controller
- --validating-webhook=:8443
- --validating-webhook-certificate=/usr/local/certificates/cert
- --validating-webhook-key=/usr/local/certificates/keymain.go
フラグのパースやサーバーの起動を実装している。
-
Kubernetesのバージョンが
v1.14.0v1.18.0と比べてログを出したりIngressClassリソースから取得したりする
v1.14.0未満ではk8s.io/api/extensions/v1beta1を使うようにログに出る
v1.18.0からはIngressClassリソースが実装されていて、kubernetes.io/ingress.classアノテーションは非推奨になった -
ヘルスチェック用のサーバー起動
-
GoやNginxのメトリクスを収集するためのCollectorの起動
$ kubectl -n ingress-nginx exec -it ingress-nginx-controller-7fd7d8df56-dv7s6 -- bash -c "curl -s localhost:10254/metrics | grep go_gc"
# HELP go_gc_duration_seconds A summary of the pause duration of garbage collection cycles.
# TYPE go_gc_duration_seconds summary
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0"} 3.58e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.25"} 9.96e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.5"} 0.0002579
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.75"} 0.0006037
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="1"} 0.009535
go_gc_duration_seconds_sum 0.0567369
go_gc_duration_seconds_count 75- pprof用のエンドポイントを生やす、デフォルトでは
10245番のポートで開放されていてここで実装されている - controllerの起動
controller.NewNGINXController にはcontrollerの実装が書かれているので次はここの実装を見る。
SIGTERM を投げることで停止されるようになっている。
ngx := controller.NewNGINXController(conf, mc)
mux := http.NewServeMux()
registerHealthz(nginx.HealthPath, ngx, mux)
registerMetrics(reg, mux)
go startHTTPServer(conf.ListenPorts.Health, mux)
go ngx.Start()
handleSigterm(ngx, func(code int) {
os.Exit(code)
})internal/ingress/controller/nginx.go
func NewNGINXController(*Configuration, metric.Collector) *NGINXController {#NewNGINXController}
EventBroadcasterの作成、ここにサンプルがあるがこれを使う事でEventsに書き込む事ができる
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()
eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)
eventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&v1core.EventSinkImpl{
Interface: config.Client.CoreV1().Events(config.Namespace),
})/etc/resolv.confからnameserverの取得- Admission Controllerの設定
store.NewでIngressやSecretといった各リソースのイベントが発火された際の処理を実装している
イベントの発火後は引数のupdateChに送信し、ここで受信する。
n.store = store.New(
config.Namespace,
config.ConfigMapName,
config.TCPConfigMapName,
config.UDPConfigMapName,
config.DefaultSSLCertificate,
config.ResyncPeriod,
config.Client,
n.updateCh,
pod,
config.DisableCatchAll)(*NGINXController).syncIngressをsyncQueueのcallback関数として指定している
キューにタスクが追加されるたびにsyncIngressが実行される
syncIngressでは実際にEndpointsを取ったりしている、ここは詳しく見ていく: nginx.go#L139
n.syncQueue = task.NewTaskQueue(n.syncIngress)- nginx.confのテンプレートの初期化
コンテナ内では/etc/nginx/template/nginx.tmplに配置されるのでConfigMapを使う事で任意のnginx.confで動かす事が可能 - GeoIPファイルの監視の設定
func (*NGINXController) Start() {#controller-start}
-
electionIDを使ったリーダー選出し、Ingressリソースのステータスを更新するPodを決める、リーダー選出はclient-goで実装されている。 -
--enable-ssl-passthroughを指定してcontrollerを起動した場合に、nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthroughアノテーションのついたリソースでSSLパススルーを行うプロキシサーバーの起動 -
Admission Controllerの起動 -
Nginxの起動 -
syncQueueの起動、Exponential Backoff によるリトライの実装 -
Nginxの起動 -
updateChから受信したイベントをsyncQueueに流す
func (*NGINXController) Stop() error
Admission Controllerの停止Nginxの停止、Nginxが停止しているかどうかはプロセスの一覧を取ってnginxという名前がないか見ているだけのシンプルな実装である
func (*NGINXController) syncIngress(interface{}) error {#syncIngress}
キューにタスクが追加されるたびにこの関数が実行される。
実行はここでしている。
- 実際にここの処理で
Endpointsを取得していることが確認できる
getConfiguration => getBackendServers => createUpstreams => serviceEndpoints
endp, err := n.serviceEndpoints(svcKey, path.Backend.ServicePort.String())- service-upstream が指定されている場合は
EndpointsではなくServiceに振られているIPを使う - テンプレートを評価し、
nginx -s reloadを実行する
Admission Controller {#admission-controller}
Admission Controller のHadnlerの実装はここでしている。
if n.cfg.ValidationWebhook != "" {
n.validationWebhookServer = &http.Server{
Addr: config.ValidationWebhook,
Handler: adm_controler.NewAdmissionControllerServer(&adm_controler.IngressAdmission{Checker: n}),
TLSConfig: ssl.NewTLSListener(n.cfg.ValidationWebhookCertPath, n.cfg.ValidationWebhookKeyPath).TLSConfig(),
}
}NGINXController は CheckIngress を実装していて、
Admission Controller がリクエストを受け取ると (*IngressAdmission) HandleAdmission(*v1beta1.AdmissionReview) が叩かれてその中で CheckIngress が叩かれる。
(*NGINXController) CheckIngress(*networking.Ingress) error
下記のような事を行なっている。
kubernetes.io/ingress.classアノテーションが起動時に指定した--ingress-classと一致するかどうか
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: application-ingress
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
spec:
backend:
serviceName: application-service
servicePort: 8080- 起動時に
--watch-namespaceを指定していた場合、指定されたNamescapeかどうか nginx -tによる生成する予定のnginx.confのテスト
Leader Election {#leader-election}
Leaderとなった Pod は Ingress のステータスを毎秒同期している。
client-go で実装されていて、 ConfigMap を使いロックをしている。
Leaderが落ちたりして renewTime の更新ができなかった場合は他の Pod が renewTime と holderIdentity を更新しLeaderに昇格する。
$ kubectl -n ingress-nginx get cm/ingress-controller-leader-nginx -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
annotations:
control-plane.alpha.kubernetes.io/leader: '{"holderIdentity":"ingress-nginx-controller-75f84dfcd7-f22xq","leaseDurationSeconds":30,"acquireTime":"2020-06-22T14:38:14Z","renewTime":"2020-07-15T18:22:19Z","leaderTransitions":0}'
creationTimestamp: "2020-06-22T14:38:14Z"
managedFields:
- apiVersion: v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:annotations:
.: {}
f:control-plane.alpha.kubernetes.io/leader: {}
manager: nginx-ingress-controller
operation: Update
time: "2020-07-15T18:22:19Z"
name: ingress-controller-leader-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
resourceVersion: "295822"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/ingress-nginx/configmaps/ingress-controller-leader-nginx
uid: 00f21dfe-d5d9-4dc0-becf-e7bbd45be4ffwait-shutdown {#wait-shutdown}
シンプルな実装だった。
err := exec.Command("bash", "-c", "pkill -SIGTERM -f nginx-ingress-controller").Run()
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("unexpected error terminating ingress controller: %v", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
// wait for the NGINX process to terminate
timer := time.NewTicker(time.Second * 1)
for range timer.C {
if !nginx.IsRunning() {
timer.Stop()
break
}
}dbg {#dbg}
デバッグ用のCLIである。
$ /dbg --help
dbg is a tool for quickly inspecting the state of the nginx instance
Usage:
dbg [command]
Available Commands:
backends Inspect the dynamically-loaded backends information
certs Inspect dynamic SSL certificates
conf Dump the contents of /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
general Output the general dynamic lua state
help Help about any command
Flags:
-h, --help help for dbg
Use "dbg [command] --help" for more information about a command.ingress-nginx-admission-create {#ingress-nginx-admission-create}
kube-webhook-certgenに実装がある。
これは何をしているかというと期限の長い自己証明書を生成してシークレットに設定してくれるやつだ。
指定されているnamespaceのSecretが存在しなかった場合のみ生成されるようになっている。
ここではAdmission Controllerの証明書を生成しようとしているのがわかる。
- name: create
image: jettech/kube-webhook-certgen:v1.2.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args:
- create
- --host=ingress-nginx-controller-admission,ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc
- --namespace=ingress-nginx
- --secret-name=ingress-nginx-admission100年後で生成されているのが確認できる。
$ kubectl -n ingress-nginx describe secret/ingress-nginx-admission
Name: ingress-nginx-admission
Namespace: ingress-nginx
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Type: Opaque
Data
====
cert: 623 bytes
key: 227 bytes
ca: 485 bytes
$ kubectl -n ingress-nginx get secret/ingress-nginx-admission -o jsonpath="{.data.ca}" | base64 --decode | openssl x509 -noout -dates
notBefore=Jun 22 14:32:42 2020 GMT
notAfter=May 29 14:32:42 2120 GMTingress-nginx-admission-patch {#ingress-nginx-admission-patch}
ではpatchは何をしているのか。
webhook-name に指定されている名前の ValidatingWebhookConfiguration を取得し、
実装としては各webhookに対して先程生成した自己証明書と failure-policy を設定している。
- name: create
image: jettech/kube-webhook-certgen:v1.2.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args:
- create
- --host=ingress-nginx-controller-admission,ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc
- --namespace=ingress-nginx
- --secret-name=ingress-nginx-admission何をしているかはわかったがこれはcreateと一緒に済ませる事ができそうな感じがしてるので
これが導入された経緯も探してみたが特に書いてないので jettech/kube-webhook-certgen についても深追いしてみる。
-
Add a validating webhook for ingress sanity check #3802
このPRでAdmission Controllerによる検証が導入された。この時点ではJobは導入されていない。 -
[stable/nginx-ingress] Add Validation webhook for nginx ingress controller #17230
このPRでhelmチャートに追加された。
jettech/kube-webhook-certgen
結論から書くと設計思想のようなものは見つける事ができなかった。
helmチャートのPRを見るとわかるが、 Implementation is inspired by the prometheus operator webhooks と書いていて 同じ仕組みで動いている。
-
[stable/prometheus-operator] PrometheusRule Admission Webhooks #14543
このPRでhelmチャートに追加された。 -
PrometheusRules Admission Webhooks
ドキュメントには上で書いていたような事がちゃんと書かれていた。